If you are facing the daunting prospect of a hip replacement you may be interested in our hip health and hip replacement blog … Before you commit to orthopaedic surgery, consider how osteopathy might be able to help. At Body@Boronia, our experienced osteopaths are here to help you improve your hip health. If surgery is necessary, we can support you both before and afterwards. Or maybe you might be able to avoid a joint replacement altogether.
Call us on 03 9762 9445 to schedule an appointment at our clinic in Melbourne’s eastern suburbs and we’ll get started on helping fix that ball-and-socket joint.
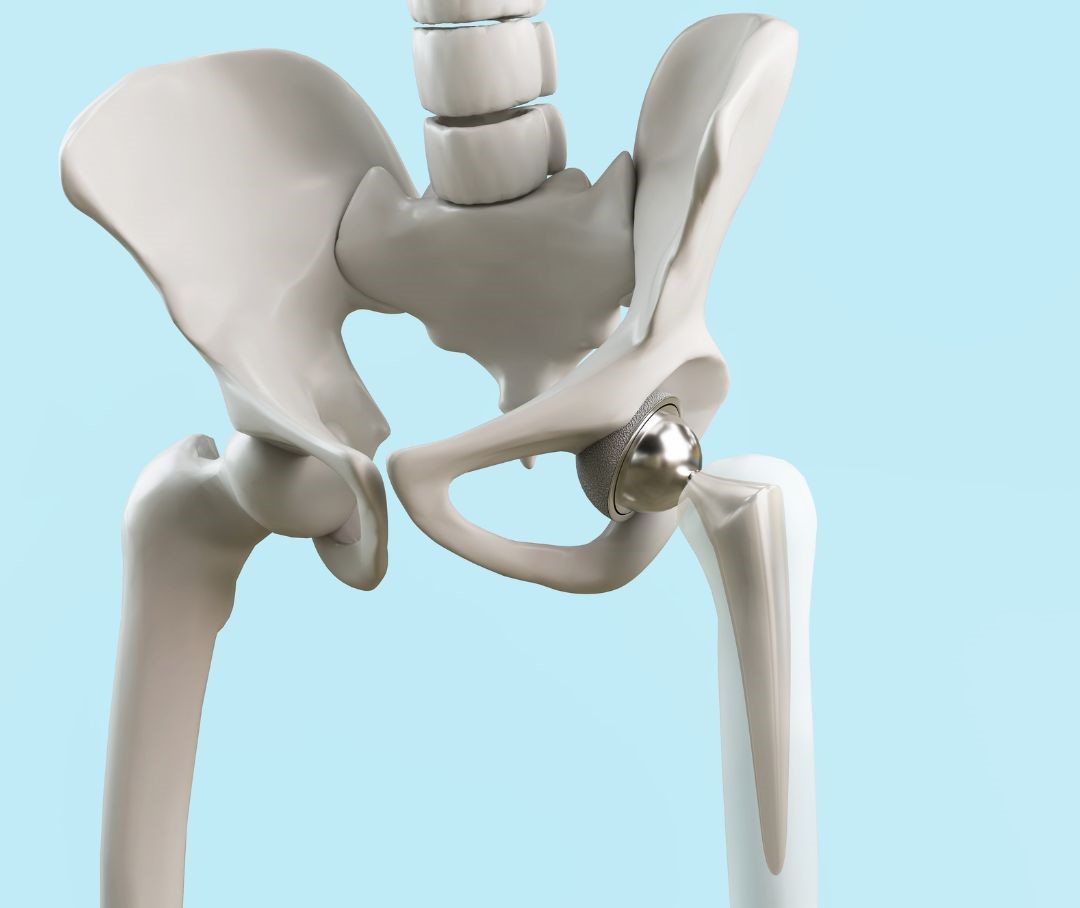
Anatomy of the Hip
The hip supports your body’s weight and allows for a wide range of motion. It is a ball-and-socket joint. The rounded head of the femur fits into the cup-like acetabulum of the pelvis, allowing for multidirectional movement and rotation. It’s a synovial joint too. That means that it’s all cushioned by a fluid-filled capsule that helps everything move smoothly and painlessly. (Or at least that’s the idea.) Over time, wear and tear, injuries, or conditions like osteoarthritis can lead to significant hip pain and reduced mobility. When the hip joint becomes severely damaged, a hip replacement, or hip repair, might seem like the only solution. However, in many cases, there are alternative approaches worth considering.
How Osteopathy Might Help
Osteopathy is a gentle, holistic system of care that focuses on the body’s musculoskeletal system. Here’s how osteopathy might help manage hip pain and delay or even avoid the need for surgery:
- Pain Management: Osteopathic treatment aims to alleviate pain through gentle manipulation, stretching, and massage. These techniques can help reduce inflammation and improve blood flow to, and drainage away from, the affected area.
- Improving Mobility: Restricted movement is a common issue with hip problems. Osteopaths work to restore range of motion through targeted exercises and adjustments, which may help you move more freely and comfortably.
- Enhancing Joint Function: By addressing imbalances and dysfunctions in the musculoskeletal system as a whole, we aim to improve the overall function of the hip joint. This can lead to better weight distribution and less strain on the hip.
- Strengthening Supporting Muscles: Weakness in the muscles surrounding the hip joint can exacerbate pain and instability. Osteopathic treatment often includes strengthening exercises tailored to your specific needs.
Conditions Treated by Osteopathy
Several hip-related conditions may respond well to osteopathic care, including:
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative joint disease causes cartilage breakdown and joint pain. Osteopathy can help manage symptoms and aims to improve joint function.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa around the hip can cause pain and swelling. Osteopathic techniques can alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
- Tendinitis: Overuse or injury can lead to inflammation of the tendons. Osteopathy can help reduce inflammation and restore tendon health.
- Muscle Strains: Strains in the muscles surrounding the hip can cause significant pain and limit movement. Osteopathic treatment can aid in recovery and prevent future injuries.
When Orthopaedic Surgery Becomes Necessary
While osteopathy offers a viable alternative to hip replacement for many, there are cases where surgery is the best option. Severe arthritis, significant joint deformities, or fractures that do not heal properly might make a joint replacement your best option. The good news is that we will give you tailored advice specific to your unique situation during your appointment and refer to you to an Orthopaedic Surgeon if necessary.
Osteopathy Pre and Post Surgery
Even when surgery is unavoidable, osteopathy can play a crucial role in pre and post-operative care:
- Pre-Surgery Preparation: Osteopathic treatments can help optimise the body’s condition before surgery. Improved mobility, reduced pain, and strengthened muscles can contribute to a smoother surgical process and better outcomes.
- Post-Surgery Rehabilitation: After a hip replacement, osteopathic care can aid in recovery. Techniques to reduce scar tissue, improve circulation, manage swelling, and restore movement may accelerate healing and enhance the function of the new joint.
Scientific Support for Osteopathy
Research supports the efficacy of osteopathy in managing musculoskeletal conditions. Studies have shown that osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) can reduce pain and improve function in patients with chronic pain conditions. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms, the evidence suggests that osteopathy can be a valuable component of a comprehensive treatment plan for hip issues.
Conclusion:
If you’ve been told you need a hip replacement, exploring osteopathic care might be a beneficial step. At Body@Boronia our skilled osteopaths are dedicated to helping you manage hip pain and improve joint function naturally. Click on the Book Online link or call us on 03 9762 9445 to book an appointment.
For more tips on injury recovery and musculoskeletal health follow us on Facebook and Instagram.
We look forward to supporting you on your journey to better hip health.
Information provided here (including text, graphics, images, outbound links, and other material) is for informational purposes only. It is general in nature and is not to be used or considered as a substitute for personalised professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your qualified allied health provider regarding any symptoms, medical conditions, or treatments and before undertaking any new health care regimen.
References
- Bagagiolo D, Rosa D, Borrelli F. Efficacy and safety of osteopathic manipulative treatment: an overview of systematic reviews BMJ Open 2022;12:e053468. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053468. [Online] Available at https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/12/4/e053468. Accessed on 31/05/2024.
- Qiong Wang, Teng-teng Wang, Xiao-feng Qi, Min Yao, Xue-jun Cui, Yong-jun Wang, and Qian-qian Liang. (2015) Manual Therapy for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pain Physician Journal. (18). [Online] Available at https://www.painphysicianjournal.com/current/pdf?article=MjQ0Mg%3D%3D&journal=92. Accessed on 31/05/2024.