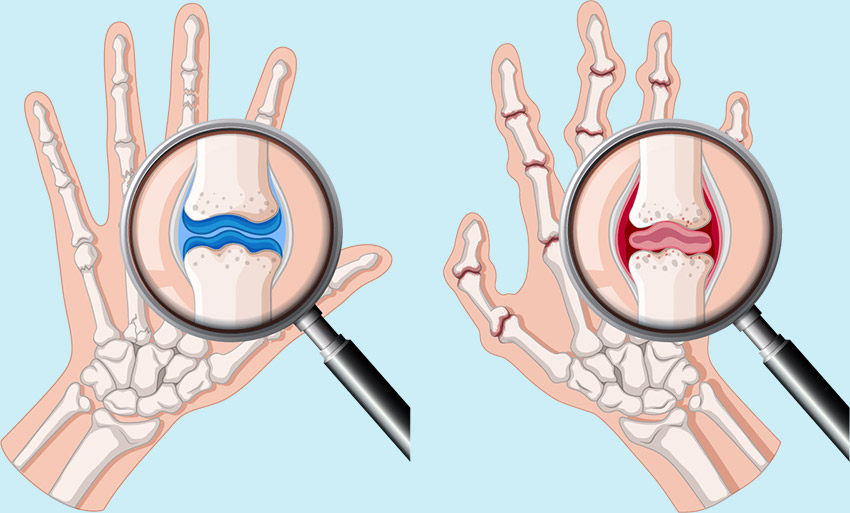
Despite being common among adults and children, arthritis is a misunderstood condition. Arthritis affects the musculoskeletal system (muscles, bones, joints) where bones meet, and includes more than 100 conditions. Symptoms vary according to the type of arthritis. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis.
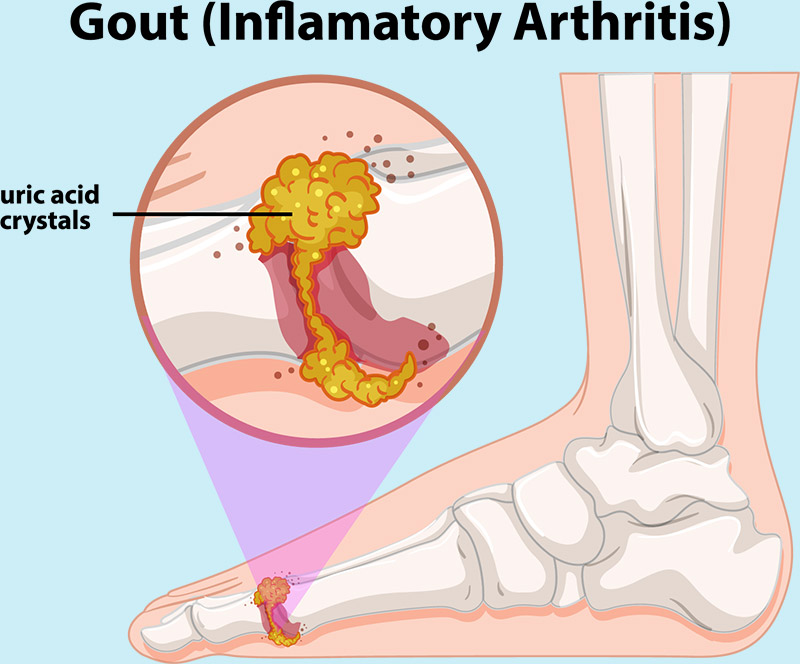
Gout
A gout attack usually happens quickly, causing inflammation, swelling and pain of the joints, often of the big toe. Hands, wrists, elbows, knees and ankles can also be affected.
Gout (part of the arthritis family) occurs when kidneys do not flush uric acid (a waste product) out of the body. A build-up of uric acid causes crystals to form in and around the joint.
Some health conditions or lifestyle factors may increase the risk of developing gout:
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Glucose intolerance
- Obesity or being overweight
- Kidney disease
- Diuretics (tablets or substances that increase water excretion from the body)
Gout runs in families; however, not all family members will be affected.
Symptoms may include:
- swollen joint – often starting with the big toe
- extremely painful joint – the weight of a bed sheet may cause intense pain
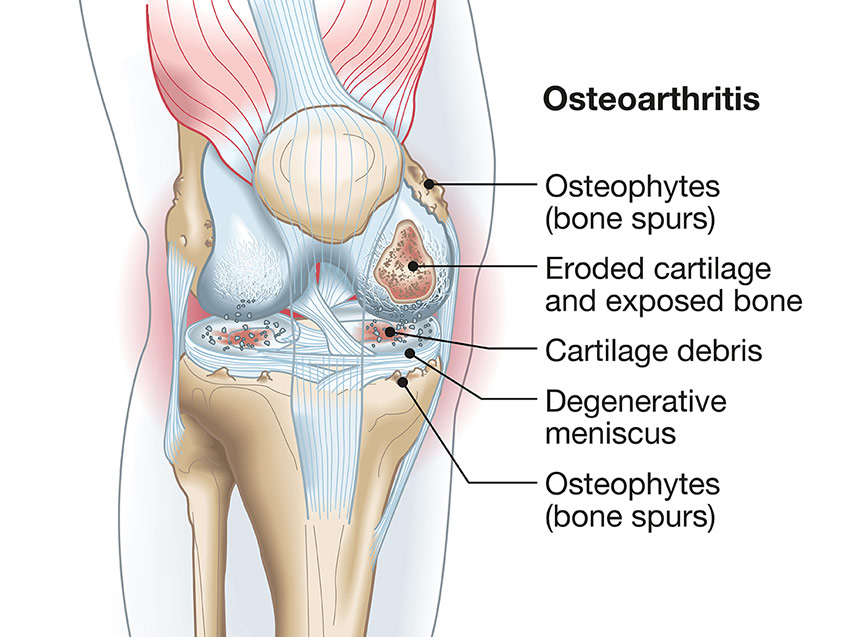
Osteoarthritis
https://arthritisaustralia.com.au/types-of-arthritis/osteoarthritis/
Osteoarthritis affects the whole joint including bone, cartilage, ligaments and muscles. It mainly occurs in knees, hips, fingers and big toe; however, it can affect any joint. The condition most likely affects people with joint injuries or aged 40 years plus. Osteoarthritis is thought to be caused by a joint attempting to repair.
Symptoms may include:
- Ligament and tendon deterioration
- Joint cartilage damage
- Joint tissue inflammation
- Bone spurs – growing around joint edge
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis are sometimes confused. For people with osteoporosis, the bones become fragile and brittle, causing them to break more easily.
Rheumatoid arthritis
https://arthritisaustralia.com.au/types-of-arthritis/rheumatoid-arthritis/
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease affecting the joints. With autoimmune disease, the immune system attacks healthy tissues. A functioning immune system should help the body fight infections.
For people with rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system targets the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and joint damage. Smaller joints in hands and feet are usually affected; however, larger joints such as hips and knees may be affected.
Symptoms may include:
- joint pain
- joint swelling
- joint tenderness
- joint stiffness – especially in the morning
- symmetrical impact (same joints on both sides of body affected)